| |
|
 | |
| MaltaWildPlants.com by Stephen Mifsud |

|
| |
|
|
 |  |  |  |
| External Links: |
|
Ballota nigra subsp. ruderalis (Black Horehound) |
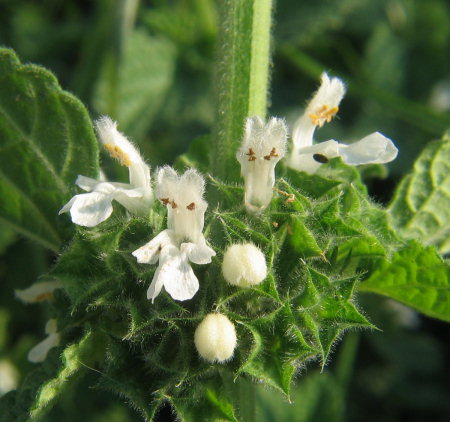

Ballota nigra subsp. ruderalis (LAMIACEAE.)
Images for this profile are taken from the Maltese Islands after year 2000. |
|
| Nomenclature |
Species name : | Ballota nigra subsp. ruderalis (Sw.) Briq. | Authority : | Olof Peter Swartz, Sweden, (1760 - 1818) ;
John Isaac Briquet , Switzerland, (1870 - 1931);
Augusto Beguinot, Italy, (1875 - 1940);
Alois Patzak, Austria, (1930- ) | Synonyms :
(basionym or principal syn.) |
Ballota ruderalis
Sw.
Synonym that was used for long in Malta:
Ballota nigra subsp. uncinata
(Bég.) Patzak
Full list of synonyms :
[Euro+Med]
[PlantList]
[IPNI]
[POWO]
[Catalogue of Life]
[Worldplants.de]
|
Plant Family : | Lamiaceae Lindl. (= Labiatae )
(Mint Family) | English name(s) : | Black Horehound, Black Hoarhound, Stinking Horehound | Maltese name(s) : | Marrubja sewda | Status for Malta : | Indigenous. Present on the Maltese islands before man | Name Derivation : |
Ballota: A Greek name given to medicinal plant Black Horehound but perhaps originating from the Greek word ballo meaning to reject, since plants were rejected by cattle. (Greek origin ); 2 = A Greek genus name given to Black Horehound (Greek) also meaning to reject "ballo" with reference that most parts of the plant are rejected by cattle (Greek);.
nigra subsp. ruderalis: 1 = Black, probably referring to the blackened leaves when plant dries. (Latin).
uncinata = Hooked or pointed at the end - referring to the calyx teeth. (Latin).
| Remarks : | |
|
| Morphology and structure |
PLANT STRUCTURE: |
Character | Growth Form | Branching | Surface |
Description | | | |
General
Picture |  | 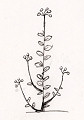 | 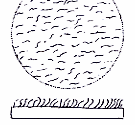 |
|
LEAVES: |
Character | Arrangement | Attachment | Venation |
Description | | | |
General
Picture | 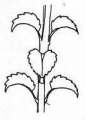 | 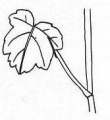 |  |
| |
Character | Leaf Shape | Leaf Margin | Remarks |
Description | | | |
General
Picture | 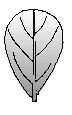 |  |  |
|
FLOWERS: |
Character | Colour | Basic Flower Type | No. of Petals | No. of Sepals |
Description | White to Lilac | | 2 Upper lip (with 2 lobes) and lower lip (having 3-4 lobes). | 1 (fused) Funnel-shape, actinomorphic calyx with 5 conspicuous subequal teeth. |
General
Picture | |  |  |  |
| |
Character | Inflorescence | Description | Ovary | Stamens |
Description | | Zygomorphic, labiate flowers which are composed of 2 lips that enclose in a tubular structure. Upper lip is slightly concave with hairs at the top part. The lower lip is glabrous and divided into 3 or 4 lobes. 4 long stamens with glabrous filaments and yellow anthers are found under the upper lip. | | |
General
Picture |  |  | 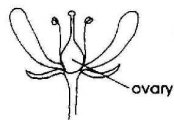 | 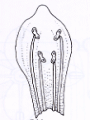 |
| |
Character | Scent | Average Flower Size | Pollen Colour | Other Notes |
Description | YES Flowers have an aromatic fragrance masked with an offensive smell coming from the whole plant. | 8 mm x 6mm Lip to lip length x depth of tube. | Yellow | - |
|
SEEDS: |
Character | No. Per Fruit | Shape | Size | Colour |
Description | 4 | Ovoid-Cylindrical Elongated cylindrical shape with a rounded end. | 2mm | Black |
General
Picture |  |  |  |  |
|
FRUIT AND OTHER BOTANICAL DATA: |
Character | Fruit Type | Colour of Fruit | Subterranean Parts | Other Notes |
Description | | Green Referring to the calyx; nutlets are black. | | Scent of Plant The plant has a mixture between aromatic and offensive smell which may vary from plant to plant. From close distances the plant's scent is generally offensive, but further away the aromatic scent is more detectable. |
General
Picture |  |  |  |  |
|
|
| Plant description and characters | |
Life Cycle: | Perennial. |
Growth Form: | HEMICRYPTOPHYTE (prostate plants with flowers close to the ground) |
Habitat: | Stony waste places, stone dumps, limestone-rich soil, or disturbed land. |
Frequency: | Scarce |
Localities in Malta: | Mriehel Industrial Estate, Wied Qirda (Zebbug). |
Plant Height: | 40-130cm. |
| Oct-Apr |
Protection in Malta: | Protected by law: Schedule VIII of [S.L. 549.44] (Exploitation subject to management measures) |
Red List 1989: | Not listed in the Red Data Book of the Maltese Islands |
Poison: | |
The herbaceous plant consists of several stems that branch at the basal part of the plant and grow up erect or tending to have an ascending position. The stems are covered by pubescent hairs and have a rectangular cross section.
Leaves are plentiful with a dark green colour. They are arranged opposite and decussate along the stems and attached to by a petiole that is shorter than the leaf blade. Leaves are rather obovate in shape with a crenated outline, measuring between 3-8cm in length and 2-6cm in width. Leaves have multi branched veins forming a net-like venation. Upper surface is conspicuously rugose (wrinkled). Leaves also possess short hairs but not as much as the stems do.
Inflorescences are found at the leaf axils and are described as verticillasters. These are a cluster of about 16 flowers resembling a whorl but in reality they consist of two cymes on opposite sides of the stem. They tend to gather at one side of the stem rather than surrounding it.
The colour of the flowers ranges from pure white to lavender. As in all labiates, the flowers are zygomorphic - consisting of 2 lip-like petals placed over each other and forming an enclosed tubular structure at one end. The upper lip is entire or has 2 small lobes at the tip and possess a tuft of hair. Lower lip is glabrous and outlined by 3 or 4 lobes. The reproductive organs include 4 stamens, made up of white glabrous filaments and yellow anthers, and a slender white style with a 2-parted stigma. Ovary is superior and hidden at the base of the calyx. The anthers are golden yellow and looks as if each is divided into 2 compartments (divergent). Corolla is 8mm long (lip to lip) and corolla tube is about 12 mm deep.
The corolla tube is held in a funnel-shaped, actinomorphic calyx with 5 subequal, slender teeth that end abruptly in a very short straight point, hence the subspecies name 'uncinata'. The calyx is about 7mm wide and 10mm long. It has many long hairs and 10 longitudinal ribs. It is attached to the stem by a very short pedicel, about 1-2mm long. There are also 5 small bracts or bractioles that are filiform and 8mm long.
The fruit consists of 4 tiny nutlets (2mm long) that are held on a common receptacle at the base of the calyx. The calyx protects these seeds during their development. When ripe, the seeds (nutlets) turn black, detach and simply fall off through the calyx with the swaying of the stems. There is no special seed-dispersal mechanism. The plant has a slight aromatic scent masked by a disagreeable odour.
|
|
| Information, uses and other details |
Nativity and distribution
The distributional range of this plant is shown in the list below: [WWW-26]
Northern Africa: Algeria [n.] ; Morocco; Tunisia
Western Asia: Cyprus; Iran; Israel; Lebanon; Syria; Turkey.
Caucasus: Armenia; Azerbaijan; Georgia; Russian Federation - Ciscaucasia, Dagestan
Europe: Denmark; Ireland; Sweden [s.] ; England; Austria; Belgium; Czechoslovakia; Germany; Hungary; Netherlands; Poland; Switzerland; Belarus; Estonia; Latvia; Lithuania; Moldova; Russian Federation - European part [s.] ; Ukraine [incl. Krym] ; Albania; Bulgaria; Greece [incl. Crete] ; Italy [incl. Sardinia, Sicily] ; Romania; Yugoslavia
Southwestern Europe: France [incl. Corsica] ; Portugal; Spain [incl. Baleares]
The Ballota are natives of the temperate regions of the Eastern Hemisphere (Western Asia) and Europe (Mediterranean region), and are remarkable for their strong offensive odour. [WWW-03]
Nomenclature
Most plants of the Ballota Genus are remarkable for their strong offensive odour, and consequently they are rejected by cattle; hence the name from the Greek ballo (to reject) [WWW-03]
It has been suggested that the name Horehound came from two Anglo-Saxon words signifying the hoary honey-yielding plant; but other authorities find other derivations. Dioscorides (like Gerard) declared that the Ballota was an antidote for the bite of a mad dog, hence the name 'hound' [WWW-03] . Species name 'nigra' - which means black - may refer to the fact that the leaves become black when they dry.
The name "marrubium" (synonym Genus name) refers to the bitter qualities of the herb, and "hoar" refers to the white pubescence covering the plant
[353]
Scent
The leaves emit a most unpleasant smell when bruised, somewhat like stale perspiration. [KF]
Medicinal Uses
The plant has the following medicinal properties according to reference: [WWW-66] .
| Adulterant |
An additive that is considered to have an undesirable effect or to dilute the active material so as to reduce its therapeutic or monetary value. [WWW-57] |
| Anti-emetic |
A medicine that prevents or alleviates nausea and vomiting, [WWW-57] |
| Antispasmodic |
Used to relieve or prevent spasms (especially of the smooth muscles) [WWW-32] |
| Astringent |
Causes shrinkage and drying of surface membranes when applied topically
. [271] |
| Condyloma |
Treats condyloma - A wartlike new growth on the outer skin or adjoining mucous membrane. [WWW-32] |
| Depurative |
An agent which is able of Purifying the blood or the humors (body fluids) [WWW-32] |
| Detersive |
A medicine used to cleanse wounds, ulcers,
etc. [WWW-32] |
| Diuretic |
Tending to increase the secretion and discharge of urine. [WWW-32] |
| Emmenagogue |
Used to promote the menstrual discharge. [WWW-32] |
| Expectorant |
Used to induce the ejection of mucus, phlegm, and other fluids from the lungs and air passages by coughing or spitting. [WWW-32] |
| Hysteria |
Treats hysteria - a state of violent mental agitation; Neurotic disorder characterized by violent emotional outbreaks and disturbances of sensory and motor functions. [WWW-32] |
| Nervine |
Substance which have the quality of acting upon or affecting the nerves causing quieting of the nervous excitement. [WWW-57] |
| Resolvent |
Has the ability to disperse inflammatory or other tumors; a discutient; anything which aids the absorption of effused products [WWW-32] |
| Sedative |
Used for making drowsy or sooth a patient, but not strong enough to induce sleep [271] |
| Stimulant |
Produces a temporary increase of vital activity in the organism, or in any of its parts; [WWW-32] |
| Stomachic |
A medicine that strengthens the stomach and excites its
action. [WWW-32] |
| Tincture |
A solution (commonly coloured) of medicinal substance in alcohol, usually more or less diluted; spirit containing medicinal substances in solution. [WWW-57] |
| Uterotonic |
An agent that overcomes relaxation of the muscular wall of the uterus; gives tone to the uterine muscle. [WWW-57] |
| Vermifuge |
A medicine or substance that expels worms from animal bodies; an anthelmintic. [WWW-57] |
Black Horehound - which should not be confused with White Horehound - is an excellent remedy for the settling of nausea and vomiting where the cause lies within the nervous system rather than in the stomach. It may be used with safety in motion sickness for example, where the nausea is triggered through the inner ear and the central nervous system. This herb will also be of value in helping the vomiting of pregnancy or nausea and vomiting due to nervousness. This remedy has a reputation as a normalizer of menstrual function and also as a mild expectorant. [WWW-08, WWW-118]
Black horehound has a long history of herbal use, though is not widely employed in modern herbalism because of its unpleasant flavour [238, 268] . Nonetheless, it does have a range of medicinal virtues, being especially effective in its action as an antiemetic [254] . In the past it was often used for treating problems connected with the respiratory system, convulsions, low spirits and the menopause, but present-day authorities differ over whether it was effective in these applications [254] .
The whole plant is antiemetic, antispasmodic, expectorant, stimulant and vermifuge [4, 165, 238] . It is taken internally in the treatment of nervous dyspepsia, travelling sickness, morning sickness in pregnancy, arthritis, gout, menstrual disorders and bronchial complaints [238, 254] .
The plant is harvested as it comes into flower and is dried for later use [238] . It should not be stored for longer than a year [238] . The fresh herb is sometimes used to make a syrup [238] .
Black horehound is believed to prevent or relieve spasms of the stomach which may also lessen nausea and vomiting. Because it also has mild sedative properties, black horehound has been used for treating "nervous" stomach associated with anxiety. Traditionally, it has been used to prevent and relieve motion sickness, although no evidence from human studies supports this use. Both its antinausea and anti-anxiety effects make black horehound useful for treating insomnia and general nervousness. In Europe, it is used commonly to relieve mild nervous conditions [WWW-49]
Topically, black horehound is used as an astringent on skin that has been irritated by insect bites, razor burn, scrapes, or sunburn. An astringent shrinks and tightens the top layers of skin or mucous membranes, thereby reducing secretions, relieving irritation, and firming tissue. Chemicals in black horehound may have mild antibacterial effects, as well. [WWW-49]
Both black and white horehound have been used to treat the bites of snakes and mad dogs, to rid the system of intestinal worms, and as antidotes to vegetable poisons. Black horehound is considered to be especially useful in quelling the nausea associated with motion sickness, or to stop the vomiting brought on by nervous tension. It also acts as an emmenagogue, restoring a healthy balance to the menstrual cycle. [WWW-119]
Constituents Chemicals
The following is a list of chemical constituents found in Ballota nigra according to reference [WWW-66] . The list includes the part(s) of the plant the constituent is found and the concentration in ppm for some important ones.
(+)-(E)-CAFFEOYL-L-MALIC-ACID - Shoot
1-OCTEN-3-OL - Plant {Concentartion: 4ppm}
13-HYDROXYBALLONIGRINOLIDE - Shoot
7-ACETOXYMARRUBIIN - Plant
7-ALPHA-ACETOXYMARRUBIIN - Shoot
7-GLUCOSIDE - Shoot
ALPHA-HUMULENE - Plant {Concentartion: 8ppm}
ALPHA-PINENE - Plant {Concentartion: 3ppm}
ALYSSONOSIDE - Shoot
ANGOROSIDE-A - Shoot
APIGENIN - Shoot
ARENARIOSIDE - Shoot
BALLONIGRIN - Plant
BALLONIGRINE - Shoot
BALLOTENOL - Plant
BALLOTENOL - Shoot
BALLOTETROSIDE - Shoot
BALLOTINONE - Plant
BALLOTINONE - Shoot
BETA-PINENE - Plant {Concentration: 1 ppm}
CAFFEIC-ACID Leaf {Concentartion: 2000 ppm}
CAFFEOYL-MALIC-ACID - Shoot
CARYOPHYLLENE - Plant {Concentartion: 35 ppm}
CHLOROGENIC-ACID - Plant
CHOLINE - Plant
COPAENE - Plant {Concentartion: 19ppm}
DELTA-CADINENE - Plant {Concentartion: 10 ppm}
EO - Plant 300ppm
FERULIC-ACID - Plant
FORSYTHOSIDE-B - Shoot
FORSYTHOSIDE-B - Shoot
GALLIC-ACID - Plant
GERMACRENE-D - Plant {Concentartion: 127ppm}
LAVANDULIFOLIOSIDE - Shoot
LINALOOL - Plant {Concentartion: 3ppm}
MARRUBIIN - Plant
PRELEOSIBIRIN - Plant
PRELEOSIBIRIN - Shoot
RAFFINOSE Root
SABINENE - Plant {Concentartion: 4ppm}
STACHYOSE Root
SUCROSE Root
TAGERETIN - Shoot
TANNIN - Plant
VERBASCOSE Root
VERBASCOSIDE - Shoot
VICENIN-2 - Shoot
[WWW-119] states that the most important constituents are the Diterpenoids (=Terpenoids having a C20 skeleton), including marrubiin, ballonigrin, ballotinone (=7-oxomarrubiin), ballotenol and 7-acetoxymarrubiin.
In laboratory studies, chemicals known as phenylpropanoids that are contained in black horehound have shown antioxidant properties. Antioxidants are thought to protect body cells from damage caused by a chemical process called oxidation, which produces oxygen free radicals, natural chemicals that may suppress immune function. Much more study is needed to prove or disprove antioxidant effects of black horehound. [WWW-49]
Black Horehound used to reduce motion sickness
Motion sickness is a disorder caused by repetitive angular and linear acceleration characterized primarily by nausea and vomiting.
Motion sickness is a syndrome that occurs in some people when they travel in a vehicle such as an automobile, airplane, or ship. Its symptoms include dizziness, nausea, vomiting, drowsiness, pallor, and sweating. Why some people experience motion sickness and others don't, is uncertain. The syndrome appears to arise from a disturbance in the organs of balance found in the inner ear. Psychological factors may also be involved. In the course of a long journey, the problem may disappear on its own, and in general such symptoms quickly cease once travel is ended.
[WWW-118]
Specific Remedies:
Ginger can usually be relied upon. Research published in the British medical journal The Lancet, showed it to be more effective than Dramamine in preventing the symptoms of motion sickness. It may be taken as a cup of fresh infusion, eaten as candied ginger, or as capsules of the powder. For people who do not like the taste of ginger the capsules are ideal, usual dosage of such capsules is 2 to 4 as needed. The herb Black Horehound (Ballota nigra) will also reduce this kind of nausea. One of the more effective allopathic treatments involves a dermal patch of scopolamine, a constituent of Belladonna.
[WWW-118]
Neurosedative and antioxidant activities of phenylpropanoids from Ballota nigra.
Ballota nigra is a European plant known for its neurosedative properties. In this study, the ability of five phenylpropanoids (verbascoside, forsythoside B, arenarioside, ballotetroside, and caffeoyl malic acid) isolated from a hydroalcoholic extract, to bind to benzodiazepine, dopaminergic, and morphinic receptors was investigated. To carry out these studies, affinity tests with rat striata, entire brains and receptor rich preparations were employed. In addition, the phenolic aspect of these five phenylpropanoid esters led to investigate antioxidant activities using cell-free experiments and cellular experiments including isolated polymorphonuclear neutrophils (PMN). Effects of phenylpropanoid esters against reactive oxygen species as superoxide anion, peroxide hydrogen, hypochlorous acid and hydroxyl radical were tested. These molecules are liberated by PMN during inflammatory disorders, so that reproduction of this process in vitro stimulating PMN by chemical stimulants was undertaken. Results show that four of the five compounds are able to bind to the studied receptors. Inhibitory concentrations at 50% were determined and vary from 0.4 to 4.7 mg/ml. This may be in relation with the Ballota nigra known neurosedative activities. Results concerning antioxidant investigations evidence an ability to scavenge reactive oxygen species. Inhibitory concentrations at 50% obtained are comparable to those of known antioxidant drugs (mesna or N-acetyl cysteine). Moreover, the use of different stimuli having various pathways of action on PMN oxidative metabolism permits to establish that each phenylpropanoid ester has its own particular way of action by using proteine kinase C or phospholipase C pathways. [354]
Isolation and antibacterial activity of phenylpropanoid derivatives from Ballota nigra.
In addition to the previously isolated phenylpropanoid glycosides verbascoside 1, forsythoside B 2, arenarioside 3 and ballotetroside 4, another four compounds were isolated from generative aerial parts of Ballota nigra: three phenylpropanoid glycosides, alyssonoside 5, lavandulifolioside 6 and angoroside A 7 and a non-glycosidic derivative (+)-(E)-caffeoyl-L-malic acid 8. The antibacterial activity of the five major compounds (1-4 and 8) was tested against gram-positive and gram-negative bacteria. Three of them (1-3) exhibited a moderate antimicrobial activity against Proteus mirabilis and Staphylococcus aureus including one methicillin-resistant strain. [355]
Properties of a close relative plant - Murrubium vulgare (White Horehound)
As a medicinal plant, horehound has traditionally been used against asthma, coughs, colds, bronchitis, sore throats, and skin irritations. The plant has also been used as a diaphoretic, diuretic, expectorant, laxative, stimulant, stomachic, tonic, and vermifuge. Horehound has been used in treatment of tumors. The volatile oil is a carminative and expectorant, while the bitter principle results in gastric activity. Consumption of large quantities of horehound can induce diarrhea and nausea.
The chief constituent of horehound is the bitter principle marrubium. Tannins, resins, waxes, and a volatile oil containing monoterpenes and a sesquiterpene have also been isolated from the plant.
The leaves and stems of horehound are often boiled and used in the preparation of candied products, cough drops, and syrups. Extracts of horehound are used in bitters and liqueurs. The plant is also grown for its ornamental value and is attractive to bees. [353]
Propagation and Cultivation
The plant grows well in waste ground, hedgerows, woods and shady places, preferring nitrogen-rich, moist, rather loose soil [13, 268] .
Prefers a well-drained soil in full sun or partial shade [134, 238] . Avoids acid soils in the wild but tolerates a pH down to 5 in cultivation [200] .
This species is not hardy in the colder areas of the country, it tolerates temperatures down to between -5 and -10°C [200] .
This species is widely grown in herb gardens, but little employed because of its strong flavour [238] . Its essential oil is used to adulterate the oil of white horehound (Marrubium vulgare) [238] . The leaves emit a most unpleasant smell when bruised, somewhat like stale perspiration [245] .
Plants can self-sow freely when well-sited [238] .
There is at least one named variety selected for its ornamental value [238] .
The whole plant has an offensive odour [4] .
Propagation is by seed or plant division. [KF]
By seed:- sow spring or autumn in a greenhouse. The seed usually germinates in 3 - 6 weeks at 15°C [134] . Prick out the seedlings into individual pots when they are large enough to handle and plant them out into their permanent positions in the summer or following autumn. [KF]
By division:- in spring. Larger divisions can be planted straight into their permanent positions whilst smaller clumps are best potted up and kept in a cold frame until they are growing away well. [KF]
Personal Observations
Variation in flower colour
The plant is almost always described to have purple to lilac flowers. The community of few plants growing close to each other, and probably originating from the same mother plant, that were found for this profile, all had white flowers. Another specimen in Wied Qirda had pale lilac flowers. Plants with purple flowers have not been encountered so far and possibly this subspecies forms whiter flowers as reported. [SM]
Below are 3 links which show pictures of the plant with purple or lilac flowers:
Plant 1: (www.dipbot.unict.it - Italy)
Plant 2: (wisplants.uwsp.edu - Wisconson US)
Plant 3: (www.boga.ruhr-uni-bochum.de - Germany)
Plant 4:
(www.rolv.no - Norway)
The subspecies uncinata
The following is a list of subspecies of Ballota nigra that have been described in history. Some may have been renamed or direct synonyms of each other:
- Ballota nigra subsp. anatolica P.H. Davis
- Ballota nigra subsp. meridionalis (Beguinot) Beguinot
- Ballota nigra subsp. nigra L.
- Ballota nigra subsp. sericea (Vandas) Patzak
- Ballota nigra subsp. uncinata (Fiori & B,guinot) Patzak
- Ballota nigra subsp. velutina (Pospichal) Patzak
- Ballota nigra subsp. foetida (Visiani) Hayek (= B. nigra subsp. meridionalis )
- Ballota nigra subsp. ruderalis (Swartz) Briq. ( = B. nigra subsp. nigra )
The subsp. uncinata is characterised by the pointed, rod-like endings of the 5 teeth of the calyx. This subspecies is confined to the Southern region of Europe, and this is the only one reported in Malta. [332]
Rare in Malta
According to Haslam's book - a flora of the Maltese islands [332] the plant is described as rare in the Maltese islands. The book was written in 1975, so after 30 years, it may be assumed that it has become rarer. Here is a list of locations that the plant has been reported in Haslam's book:-
Malta: Dingli, Ghammieri, Burnuhhala, Pwales, St.Paul's Bay, Selmun, Addolorata Cemetery valley, Sa maison.
Gozo: Munxar, Capuchini convent, Xlendi, Xewkija. [332]
The photos for this plant profile were taken by few plants close to each other in the industrial estate of Mriehel, on the 31st October 2005. The plants are prone to disappear because the land looks to be aimed for building construction sooner or later. Few other specimen where found scattered at Wied Qirds later in October 2005. [SM]
Closely related species - Melissa officinalis
B. nigra is very similar in appearance to a famous medicinal plant - Melissa officinalis. It has the same length, habitat, growth habit and similar leaves - obovate, petiolate, crenate and wrinkled surfaces. The flowers are similarly borne in clusters at leaf axils and can be white/cream to pale purple. The main difference is the shape of the calyx and fine details of the flower as shown in the table below which compares the 2 related plants. [SM]
| Feature |
Ballota nigra subsp. uncilata |
Melissa officinalis |
| Calyx symmetry |
Actinomorphic |
Zygomorphic |
| Calyx teeth |
Pointed but not spiny |
Blunt |
| Hairs on upper lip of flower |
Present |
Absent (Mostly glabrous) |
| Shape of upper lip |
Entire or slightly notched at the apex |
Divided into 2 lobes (bifid) |
| Scent |
Offensive despite slightly aromatic |
Pleasing lemon-like aromatic smell |
|
|
| Links & Further literature
(0 papers) |

Google Web |

Google Images |

Google Scholar |

Research Gate |

Wikipedia |

JSTOR |

GBIF |

Med Checklist |

Cat. of Life |

EoL |

IPNI |

World Flora Online |

Plants of the World Online |

Vienna Virt. Herb. |

RBGE Herbarium |

KEW Herbarium |

MNHN |

Arkive |

IUCN |

CABI |
Kindly Email if there are papers and publications about local
studies or information about this species to be included in the list above.
|
| Photo Gallery (44 Images) |  |
 |
 |
 |
IMAGE: BLTNR-01 Photo of flowers. Colour could be white, lilac or pale purple. |
IMAGE: BLTNR-02 Photo of flowers. They measure around 8mm from lip to lip and the corolla tube is 10mm deep. |
IMAGE: BLTNR-03 Photo of flowers and buds. Flowering time between October and November. |
IMAGE: BLTNR-04 Photo of flowers. They are found in clusters where there are about 2 to 6 open flowers. Whole cluster contains about 8-18 buds. |
 |
 |
 |
 |
IMAGE: BLTNR-05 Photo of 2 flowers and several calyces that have a star-shaped mouth. |
IMAGE: BLTNR-06 Close up photo of flowers. They are bi-laterally symmetrical (zygomorphic) with 2 lips placed over each other which join and form a tubular structure located inside the calyx. |
IMAGE: BLTNR-07 Photo of flowers. They are borne in clusters at the leaf axils close to the stem. |
IMAGE: BLTNR-08 Lateral view of flower showing the tuft of white hair on the upper lip and the reproductive organs (4 stamens + 1 style) just below the upper lip. It can be clearly seen that the stigma is bifid (splits in two parts). |
 |
 |
 |
 |
IMAGE: BLTNR-09 Close up photo of the zygomorphic flower and actinomorphic calyx opening. |
IMAGE: BLTNR-10 Close up photo of flower showing the stamens with tobacco-yellow anthers. Top part of upper lip possesses many white hairs. |
IMAGE: BLTNR-11 Close up photo of flower. Lower lip has 3 (as shown in this photo) or often 4 lobes. |
IMAGE: BLTNR-12 Photo of 2 flowers, with the one on the right having 4 lobes at its lower lip. |
 |
 |
 |
 |
IMAGE: BLTNR-13 Photo of a row of pink flowers found on a group of plants at Wied Qirda (Zebbug). |
IMAGE: BLTNR-14 Close up photo of 2 pink flowers. |
IMAGE: BLTNR-15 Close up photo of a pink flower framed around a number of trumpet-shaped calyces. |
IMAGE: BLTNR-16 Another close up photo of the flower. |
 |
 |
 |
 |
IMAGE: BLTNR-17 Macro photo of stamens. They have a rather glabrous white filament and a dark yellow anther which is split in 2 distinct diverging bodies. |
IMAGE: BLTNR-18 Scanned image of 3 flowers at different planes or angles of view. Left to Right: Upper Lip / Lower lip / Lateral view. |
IMAGE: BLTNR-19 Scanned and annotated image of flower. |
IMAGE: BLTNR-20 Scanned image of dorsal view of flower (forced open). |
 |
 |
 |
 |
IMAGE: BLTNR-21 Scanned image of a dissected flower showing its 2 lips, stamens and style. |
IMAGE: BLTNR-22 Scanned image of the leaves and flower cluster that grows from the axils of the leaves. |
IMAGE: BLTNR-23 Scanned image of lower side of leaves and clusters showing the anatomy of the flowers. This photo shows clearly the short flower stalklet (1mm), the thin, filiform bract (or bractiole) that measures about 8mm long, and the trumpet shaped calyx (10mm long). |
IMAGE: BLTNR-24 Scanned image of leaves and flower showing their arrangement. Leaves are not perfectly opposite (180° ) but at an angle to each other. In the obtuse angle there are the flower clusters while at the acute (smaller) angle there are found 2 leaflets. |
 |
 |
 |
 |
IMAGE: BLTNR-25 Photo of the hairy calyx. It is funnel shaped, 10mm long, with 10 longitudinal ribs. |
IMAGE: BLTNR-26 Scanned image of calyx. Actinomorphic, star shaped, 5 sub-equal teeth with an elongated ending like a rod. For this reason comes the sub-species name uncinata which means ending with a hook or rod. |
IMAGE: BLTNR-27 Photo of leaves. Opposite and decussate (each row is perpendicular to the one above/below) and a conspicuously wrinkled surface. |
IMAGE: BLTNR-28 Close up photo of the surface of the leaf. |
 |
 |
 |
 |
IMAGE: BLTNR-29 Scanned image of leaves. They are obovate, have a crenated outline and a rather short petiole. Venation is highly branched - like a net. |
IMAGE: BLTNR-30 Photo of plants in their habitat, usually rocky or stony wasteland or disturbed ground. Plant is rare but on the increase. |
IMAGE: BLTNR-31 Photo of plants. They produce numerous erect (or ascending) stems. Branching occurs only at the basal part of the main stem. |
IMAGE: BLTNR-32 Photo of the central part of plant bearing axillary flower clusters. |
 |
 |
 |
 |
IMAGE: BLTNR-33 Photo of the upper part of plant. |
IMAGE: BLTNR-34 Another photo of the upper part of plant. |
IMAGE: BLTNR-35 Scanned image of small branch of plant. |
IMAGE: BLTNR-36 Scanned image of main stem of plant. |
 |
 |
 |
 |
IMAGE: BLTNR-37 Scanned image of foliage at the upper part of plant. |
IMAGE: BLTNR-38 Scanned image of stem which has a squarish cross section and a central hollow. It also has numerous white pubescent hairs - hairs that droop downwards. |
IMAGE: BLTNR-39 Photo of fruit which basically consists of 4 nutlets at the base of the calyx. |
IMAGE: BLTNR-40 Scanned image of seeds (nutlets). Glabrous, polished and black when fully ripe. 2mm long. 4 nutlets per fruit sitting on a common receptacle. |
 |
 |
 |
 |
IMAGE: BLTNR-41 Photo of seedlings, germinated on 15th January 2008. |
IMAGE: BLTNR-42 Photo of the seven spotted ladybird (Coccinella septempunctata) found on the plant. |
IMAGE: BLTNR-43 |
IMAGE: BLTNR-44 Black and White illustration of the plant and its floral parts from USDA.gov. |
|
| | |

