| |
|
 | |
| MaltaWildPlants.com by Stephen Mifsud |

|
| |
|
|
 |  |  |  |
| External Links: |
|
Gladiolus italicus (Field Gladiolus) |
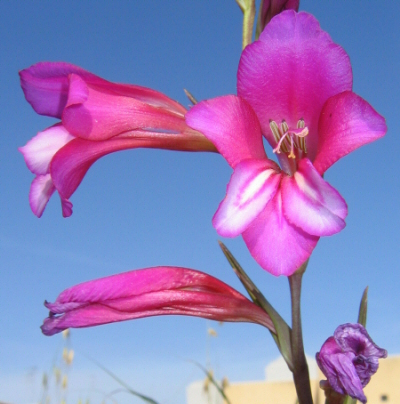

Gladiolus italicus (IRIDACEAE.)
Images for this profile are taken from the Maltese Islands after year 2000. |
|
| Nomenclature |
Species name : | Gladiolus italicus Mill. | Authority : | Philip Miller, England, (1691 - 1771) | Synonyms :
(basionym or principal syn.) |
|
Plant Family : | Iridaceae Juss.
(Iris Family) | English name(s) : | Field Gladiolus, Italian Gladiolus, Cornfield Gladiolus | Maltese name(s) : | Ħabb il-qamħ tar-raba | Status for Malta : | Archeophyte. Non-native species, but introduced in Malta before 1492 (Columbus'
discovery of the New World) but usually been on the Islands more than 1000 years. | Name Derivation : |
Gladiolus: a little sword, referring to the sword-shaped leaves of plants in this genus. (Latin origin ); 2 = "little sword" referring to the shape of the leaves (Latin);.
italicus: originating from or related to Italy, for example described first from Italy. (Latin origin ); 2 = of Italian origin, related to Italy (Latin).
| Remarks : | |
|
| Morphology and structure |
PLANT STRUCTURE: |
Character | Growth Form | Branching | Surface |
Description | | | |
General
Picture | 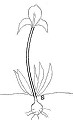 |  |  |
|
LEAVES: |
Character | Arrangement | Attachment | Venation |
Description | | | |
General
Picture | 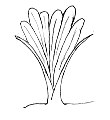 |  | 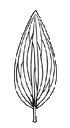 |
| |
Character | Leaf Shape | Leaf Margin | Remarks |
Description | | | |
General
Picture |  | 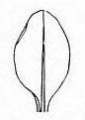 |  |
|
FLOWERS: |
Character | Colour | Basic Flower Type | No. of Petals | No. of Sepals |
Description | Purple (with white streaks). | | 6 To be botanically precise, the flower has 3 sepals (outer whorl) and 3 petals (inner whorl) which are identical, and so they are collectively referred to as 6 tepals or perianth segments. | 0 (There are two leaf-like bracts which might be confused as sepals). |
General
Picture | |  |  |  |
| |
Character | Inflorescence | Description | Ovary | Stamens |
Description | | The corolla consists of 6 tepals (= identical petals and sepals) having an intense purple colour. They are fused together at their base. The 3 lower tepals have a decorative, white, flame-like central band. The stamens have pink filaments and longer golden anthers. The white or pink style is longer by few mm and has a 3-parted feathery stigma. | | |
General
Picture |  |  | 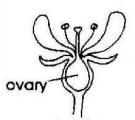 | 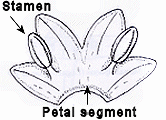 |
| |
Character | Scent | Average Flower Size | Pollen Colour | Other Notes |
Description | Mild sweet scent | 35 x 32 x 40 mm approx (L x B x H). | Pale Yellow | - |
|
SEEDS: |
Character | No. Per Fruit | Shape | Size | Colour |
Description | 24-48 | Oval/Globular shape with flaps The roundish, but not perfectly spherical seeds are enveloped in a thin flap-like structure. | 3-4mm | Orange-Brown They get darker when they dry further up. |
General
Picture |  |  |  |  |
|
FRUIT AND OTHER BOTANICAL DATA: |
Character | Fruit Type | Colour of Fruit | Subterranean Parts | Other Notes |
Description | | Green Turns light brown when mature. | | - |
General
Picture |  |  | 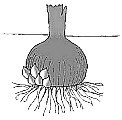 |  |
|
|
| Plant description and characters | |
Life Cycle: | Perennial. |
Growth Form: | GEOPHYTE (bearing underground bulbs, rhizomes, stolons, etc.) |
Habitat: | Cultivated fields (esp. wheat, corn etc.), fallow fields |
Frequency: | Scarce |
Localities in Malta: | Commonly spotted besides (or in) fields such as at Dingli (near Savio College), Mistra, Qormi, Bahrija, Kuncizzjoni and Wied il-Ghasel. |
Plant Height: | 50-100cm. |
| Mar-Apr |
Protection in Malta: | Not legally protected till the last update of this website (2/Mar/2022) |
Red List 1989: | Not listed in the Red Data Book of the Maltese Islands |
Poison: | |
This perennial monocotyledon plant from the Iris family grows from an underground bulb which flowers in the beginning of Spring. The plant is glabrous and unbranching.
The leaves are sword-shaped, have entire margins and parallel bulging veins. The leaves, which grow directly from the underground bulb can reach a length of up to 60-65 cm and their widest part is 1.5cm which gradually tapers up till the pointed apex. The sessile leaves grow in the same plane and emerge from same overlapping locus hence forming a 'V-shaped' structure.
In late winter, the central flower stalk emerges through the overlapping leaves and forms a spike of flowers - the bottom ones opening first. The flower contains no sepals, but there are 2 leaf-like bracts which initially, they cover and protect the bud, and later they support the flower and the developing fruit. Initially (in the bud phase) the bracts are approximately of the same length, but then one of the bracts gets longer during the blooming, flowering and fruiting phase until it becomes about 8-9cm hence 3-4 times the length of the other bract.
The spike produces 12 flowers or more. Each bi-laterally symmetrical flower is formed by 6 purple-red tepals. The tepals are not similar to each other. The largest one is at the top but it is also the least attractive. The lower 3 tepals are smaller and, especially the lateral ones, are decorated by a central, flame-like white streak with a darker purple border. Although the corolla can be described to be funnel shaped (since the tepals are fused together), they are fused together only at their base, hence the tepals have some independant appearance.
The pistil is made up of an inferior ovary, a long (c. 35mm) white to pink style and 3-parted pink to pale purple feathery stigma. The 3 stamens are somehow more conspicuous, having each an anther with a pod-like shape, 15mm long, grayish yellow-brown colour with 2 yellow slits at the underside from which pollen is liberated. The anthers are supported by thin purple to pink filaments, which are shorter than the anthers by 2-3 mm.
The fruit is a 3-bulged green capsule which drops its wingless (or short appandeged) orange-brown seeds when they ripen. If the seeds are unsuccessful, the plant will grow again next season from the perennial roundish bulb, but doing so there will be no genetical combination - it is the asexual form of reproduction.
|
|
| Information, uses and other details |
Nativity
Many Gladiolus species are derived from South Africa, but the G. italicus is native to the Mediterenean [WWW-58]. The species name italicus may indicate that it has originated from Italy. [SM]
Gladiolus italicus as a weed
There has been a study by Colasante M et al who stated that this plant and G. byzantinus, amongst others, can become invasive of wheat crops.
especially if they are left uncontrolled. The crop and the plant have similar leaves so it makes it more difficult for farmers to distinguish between the two at early stage of harvesting. [303] The full citation can be viewed here
Personal Observations
No information was found about medicinal properties, toxic properties or edible uses. The bulbs of other Gladiolus species have been used as a source of starch in famine conditions but there have been no definite reports for known traditional edible uses of the plant. [SM].
Not much information has been found about this particular plant species. If you can supply further info to be included in this profile, please do not hesitate to email us pr by using the form found at the botom of this page. Full reference credits will be given accordingly. Thank you for your support!
|
|
| Links & Further literature
(1 papers) |

Google Web |

Google Images |

Google Scholar |

Research Gate |

Wikipedia |

JSTOR |

GBIF |

Med Checklist |

Cat. of Life |

EoL |

IPNI |

World Flora Online |

Plants of the World Online |

Vienna Virt. Herb. |

RBGE Herbarium |

KEW Herbarium |

MNHN |

Arkive |

IUCN |

CABI |
 |
Preliminary observations from long-term studies of Gladiolus L. (Iridaceae) for the Maltese Islands |
Stephen Mifsud & Anthony Hamilton (2013) |
Kindly Email if there are papers and publications about local
studies or information about this species to be included in the list above.
|
| Photo Gallery (36 Images) |  |
 |
 |
 |
IMAGE: GLDIT-01 Photo of purple flower in situ. |
IMAGE: GLDIT-02 Photo of flower against sky. |
IMAGE: GLDIT-03 Detailed photo of flower and its stamens and stigma. |
IMAGE: GLDIT-04 Photo of a young flower. |
 |
 |
 |
 |
IMAGE: GLDIT-05 Photo of flower - lateral view. |
IMAGE: GLDIT-06 Photo of flowers which grows as a spike. The lower buds bloom first, followed gradually by the ones above. |
IMAGE: GLDIT-07 Photo of flower spikes - each spike may produce 12 or more flowers in healthy plants. |
IMAGE: GLDIT-08 Photo of flower spike taken in a photo studio showing a front view of a mature flower and lateral view of others. |
 |
 |
 |
 |
IMAGE: GLDIT-09 Scanned image (front view) of a flower spike showing the bracts, and the growth of flowers at an alternate (or zig-zag) way along the main flower stalk, and the upper buds. |
IMAGE: GLDIT-10 Scanned image of a lateral view of a flowering spike, clearly showing that the lower flowers bloom first, while the buds are at the top. |
IMAGE: GLDIT-11 Scanned image of few flowers to show the 2 leaf-like bracts that each flower posses. In mature flowers, one of the bracts grows longer, while in buds they are about the same length. |
IMAGE: GLDIT-12 Scanned and large image of a flower (front view). |
 |
 |
 |
 |
IMAGE: GLDIT-13 Scanned image of the 6 tepals (= 'petals') dissected out to show details of their full length. They are placed according to the position in the flower. The upper petal is the largest, while the lower ones are the most attractive with their central white streak. |
IMAGE: GLDIT-14 Magnified scanned image of the upper petals. |
IMAGE: GLDIT-15 Magnified scanned image of the upper tepals. They (especially the lateral ones) possess a decorative, central, white, flame-like, streak with a thin border of dark purple colour. |
IMAGE: GLDIT-16 Scanned image of a row of 5 lower and lateral tepals taken from different species of flowers to show the variation amongst each other. |
 |
 |
 |
 |
IMAGE: GLDIT-17 Close up photo of central part of flower showing in detail the 3 pod-shaped gray/brown stamens. |
IMAGE: GLDIT-18 Close up photo of central part of flower showing in detail the 3-parted feather-like pink/purple stigma. |
IMAGE: GLDIT-19 Scanned image of the sexual organs of the flower. The 3 stamens consist of pod-shaped anthers each with 2 yellow slits at the underside from where pollen is liberated. The pistil is made up of a green, inferior ovary (not part of the dissection), and long, slender style and a 3-parted pink stigma above the stamens. |
IMAGE: GLDIT-20 Magnified scanned image of stamens showing the 2 underside slits with pale yellow pollen. This species has the anthers longer by few mm from their supporting filaments. |
 |
 |
 |
 |
IMAGE: GLDIT-21 Magnified scanned image of the stigma. It is divided into 3 pink, feather-like branches which turns into a darker purple when mature. |
IMAGE: GLDIT-22 Magnified scanned image of style and stigma which is about 32-35mm in length. The base of the style is white and turns gradually to pink/purple towards the stigma. |
IMAGE: GLDIT-23 Scanned image of buds. The 2 leaf-like supporting and protective structures are not sepals but specialized bracts. |
IMAGE: GLDIT-24 Close up photo of the flower taken at mid April 2006. |
 |
 |
 |
 |
IMAGE: GLDIT-25 Photo of leaves in situ. They face the same plane and have a V-shaped orientation. |
IMAGE: GLDIT-26 Photo of a leaves at the locus where they emerge and out-fold from each other hence splitting apart at a small angle. |
IMAGE: GLDIT-27 Scanned image of leaves at the point where the leaves emerge from each other as overlapping folds and aplit to opposite directions at an acute angle. |
IMAGE: GLDIT-28 Scanned image of a single leaf blade which has the shape of a sword (ensiform), an entire margin and bulging but slender parallel veins. |
 |
 |
 |
 |
IMAGE: GLDIT-29 Photo of 2 plants in situ. |
IMAGE: GLDIT-30 Photo of a typical plant growing at the border of a wheat field. |
IMAGE: GLDIT-31 Photo of a flowering spike in situ. |
IMAGE: GLDIT-32 Photo of back side of spike and plant. |
 |
 |
 |
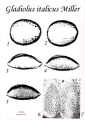 |
IMAGE: GLDIT-33 Unripe fruit capsules along flower stem. They are about 18mm long and are bulged from 3 places. The long leaf-like flap is one of the 2 bracts which previously played a part in covering the bud. |
IMAGE: GLDIT-34 Scanned image of ripe fruit, split open and liberating their orange brown seeds. As it is shown, the fruit are divided into 3 compartments each bearing 2 rows of seeds. |
IMAGE: GLDIT-35 Scanned image of the orange-brown seeds. |
IMAGE: GLDIT-36 Magnified image of pollen under microscope. It is bilaterally symmetrical and has an oval flattened shape, (like a cushion). Taken from Flora apistica della Sicilia (by Prof. Nunzio Longhitano). |
|
| | |

