| |
|
 | |
| MaltaWildPlants.com by Stephen Mifsud |

|
| |
|
|
 |  |  |  |
| External Links: |
|
Glebionis coronaria (Crown Daisy) |
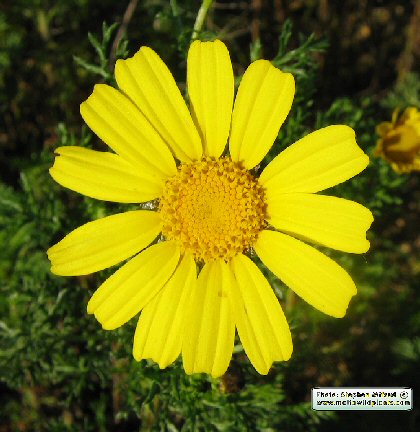

Glebionis coronaria (ASTERACEAE.)
Images for this profile are taken from the Maltese Islands after year 2000. |
|
| Nomenclature |
Species name : | Glebionis coronaria (L.) Cass. Ex Spach. | Authority : | Carl von Linne, Sweden, (1707 - 1778) ;
Alexandre Henri Gabriel de Cassini, France, (1781 - 1832);
Edouard Spach, France (1801 - 1879) | Synonyms :
(basionym or principal syn.) |
|
Plant Family : | Asteraceae Bercht. & J.Presl (= Compositae )
(Daisy or Sunflower Family) | English name(s) : | Crown Daisy, Garland, Chop Suey Greens | Maltese name(s) : | Lellux | Status for Malta : | Indigenous. Present on the Maltese islands before man | Name Derivation : |
Glebionis: Latin gleba meaning soil, but allusion remains unclear, perhaps for preferring agricultural habitats with plenty of soil. (Latin origin ); 2 = (unknown derivation)
the previous and more popular Genus name for this plant was Chrysanthemum which is derived from "chrysos" which means gold (Greek) and "anthemon" which means flower (Greek), hence "golden-flower".
coronaria: Coming from the word corona which means a crown and possibly referring to the golden and crown-shaped flower. (Latin origin ); 2 = "corona" = crown, refering to the large flower head (Latin).
| Remarks : | - |
|
| Morphology and structure |
PLANT STRUCTURE: |
Character | Growth Form | Branching | Surface |
Description | | | |
General
Picture |  |  |  |
|
LEAVES: |
Character | Arrangement | Attachment | Venation |
Description | | | |
General
Picture |  |  |  |
| |
Character | Leaf Shape | Leaf Margin | Remarks |
Description | | | |
General
Picture |  |  |  |
|
FLOWERS: |
Character | Colour | Basic Flower Type | No. of Petals | No. of Sepals |
Description | Golden Yellow Some variaties have the upper half or third of the petal white (G. coronaria var. discolor). | | 12-15 | 20-32 Referring to the phyllaries of the involucre. |
General
Picture | |  |  |  |
| |
Character | Inflorescence | Description | Ovary | Stamens |
Description | | Bright golden-yellow flower consisting of a cluster of central, yellow disc-florets (maturing from circumference to center) and 12 to 15 radiating golden-yellow petals (ray-florets), which occasionally have white tips. | | |
General
Picture |  |  | 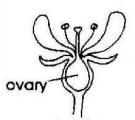 | 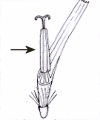 |
| |
Character | Scent | Average Flower Size | Pollen Colour | Other Notes |
Description | YES Strong, camomile-like, pleasant scent. | 35 mm (ref. to the whole flower head). | Yolk yellow | - |
|
SEEDS: |
Character | No. Per Fruit | Shape | Size | Colour |
Description | 100-200 (1 per floret, 100-200 florets per flower head). | | 2-3mm | Light brown |
General
Picture |  |  |  |  |
|
FRUIT AND OTHER BOTANICAL DATA: |
Character | Fruit Type | Colour of Fruit | Subterranean Parts | Other Notes |
Description | | Brown (referring to the achenes colour). | | Scent The plant, especially the flowers and seeds, gives off a certain strong scent of aromatic chamomille. |
General
Picture | 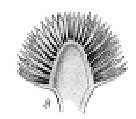 |  |  |  |
|
|
| Plant description and characters | |
Life Cycle: | Annual. |
Growth Form: | THEROPHYTE (annual plants, herbaceous) |
Habitat: | Fallow fields, waste ground, soil dumps, field margins, footpaths, soil mounds |
Frequency: | Common |
Localities in Malta: | Very Common throughout the islands. Could be classified as the most abundant plant during late spring. |
Plant Height: | 20-75cm. |
| Jan-May |
Protection in Malta: | Not legally protected till the last update of this website (2/Mar/2022) |
Red List 1989: | Not listed in the Red Data Book of the Maltese Islands |
Poison: | |
This tall, eye catching annual has large flower heads up to 60mm diameter, and frequently grows in abundance creating a mass of golden yellow carpets in many places around Malta and Gozo. Occasionally, some flowers from the other variant are seen. These have a yellow center and whitish outer tips.
 Its stems are erect and hairless, and forms numerous compound branches. The oblong or lance-shaped multi pinnate or pinnatifid leaves can be over 10cm long. Each pinna (leaf lobe) can further have smaller lobed projections.
Its stems are erect and hairless, and forms numerous compound branches. The oblong or lance-shaped multi pinnate or pinnatifid leaves can be over 10cm long. Each pinna (leaf lobe) can further have smaller lobed projections.
The flower heads are supported by thickened stalks, and overlapping, short, triangular shaped phyllaries, which often have a dark outline. The flower heads have a central flattened, disc-shaped receptacle holding many yellow, tubular disc-florets and the perimeter is outlined by 10-15 ray-florets with large (20mm) golden yellow 'petals'. The reproductive organs (stamens and style) lie within every floret. The 5 stamens are fused together as a singular collar around the style. The florets at the perimeter mature first and those of the center last.
The fruit is a simple tooth-like achene, without a pappus. No particular seed dispersal mechanism. They fall down on the soil and many times they are carried away by ants down into the soil. Each plant forms numerous flowers, and hence it can produce several thousands of seeds.
|
|
| Information, uses and other details |
Nomenclature
The scientific genus name of the plant is recently changed from Chrysanthemum to Glebionis [WWW-26]. Many books and even Internet documents refer to this plant as Chrysanthemum, which was its genus name for many years. However there was a nomenclature update and Chrysanthemum now applies to the Asian genus previously treated as Dendranthema and the two Mediterranean species (C. coranarium and C. segatum) must be treated under the genus name Glebionis. [SL].
Cultivation Notes:
Succeeds in ordinary garden soil [1] , but it prefers a well-drained fertile soil in full sun [200, 206] . It will tolerate light shade in the summer. Tolerates a pH in the range 5.2 to 7.5. Plants do not grow well at temperatures above 25° C, tending to become bitter in hot weather. Plants withstand light frosts [206] . Commonly grown as an ornamental in the West, the var spatiosum is commonly cultivated as a vegetable in China and Japan [200] . There are many named varieties [183] . It takes 4 - 5 weeks from sowing the seed to the first harvest when plants are grown on the cut and come again principle [206] . Plants often self-sow when they are well-sited and the soil is disturbed by hoeing etc. [KF]
Planting:
- This plant variety generally cannot be successfully grown in areas where the soil quality is of a poor standard, ie lacking in sufficient nutrients.
- This plant variety does not tolerate heavy clay soils.
- This variety can be grown in anything from a light to a heavy soil mixture.
- For optimal results it is preferable to plant in a well drained soil.
- This variety prefers a semi shade to full sun position.
- It is preferable to plant this variety in a moist position. [WWW-01]
Medicinal Uses: The leaves are expectorant and stomachic [218] . In conjunction with black pepper it is used in the treatment of gonorrhea. The flowers are aromatic, bitter and stomachic. They are used as a substitute for camomile (Chamaemelum nobile). The bark is purgative, it is used in the treatment of syphilis. [240]
Derivatives from plant
Consolacion Y. et al discovered that A Bioactive Thiophene Derivative can be derived from from Chrysanthemum coronarium. The abstact says:
"The CHCl3 extract of the air-dried leaves of Chrysanthemum coronarium afforded N-isobutyl-6-(2-thiophenyl)-2,4-hexadienamide (1). The structure of 1 was determined by extensive 1D and 2D NMR spectroscopy and high resolution mass spectrometry and comparison with published literature. Antimicrobial tests on 1 by the agar well method indicated that it has low activity against B. subtilis, P. aeruginosa, C. albicans and T. mentagrophytes and is inactive against S. aureus and E coli at a concentration of 20 ?g. Micronucleus test indicated a 66.5% reduction in MPCE induced by Mitomycin C. Thus, 1 is an antimutagen. " [301]
Edible Uses:
Young shoots and stems - raw or cooked [34, 46, 61, 105, 116] . Strongly aromatic [183, 200] , they are used as a flavouring or as a vegetable. Cooked leaves become bitter if overcooked at a high temperature. Young leaves are excellent in salads. The leaves quickly wilt once they have been picked so it is best to harvest them as required [206] . They contain about 1.85% protein, 0.43% fat, 2.57% carbohydrate, 0.98% ash. They are rich in vitamin B1, contain a moderate content of vitamin C and a little vitamin A. [179]
Flowers - raw. Blanched briefly and added to salads [183] . The centre of the flower is bitter so only the petals are normally used [206] . A fragrant pickle known as 'kikumi' is made from the petals in Japan. [183]
Other Uses:
Possibly a good companion plant, protecting neighbouring plants from caterpillars etc. [KF]
There is a report that secretions from the roots can be effective in controlling nematodes in the soil, but this has not been substantiated. [206]
Personal Observations:
- This plant is one of the most common plants found around the whole islands of Malta, probably the second one after the Bermuda Buttercup.
- It is one of the main plants responsible for the formation a carpet of yellow areas mainly in Feb / Mar.
- The white flower variant is not so common - the yellow predominates in Malta. The white-tipped flowers tend to show up and be more common in late Spring
- Very strong plant, found even in small quantities in the driest months of June and July.
- Flowers have a pleasant smell of camomile
- Traditionally children used to play "You love me, love me not" by striping the petals one by one!!! Although flowers are abundant, such education should be discouraged. [SM]
|
|
| | |

